Treatments
Pigmentation
Pigmentation
What is Pigmentation?
Pigmentation of the skin varies according to racial origin and amount of sun exposure. The pigment cells are located at the base of the epidermis and produce melanin. Melanin then moves to the skin surface. More melanin is produced when the skin is injured e.g. following exposure to UV light.
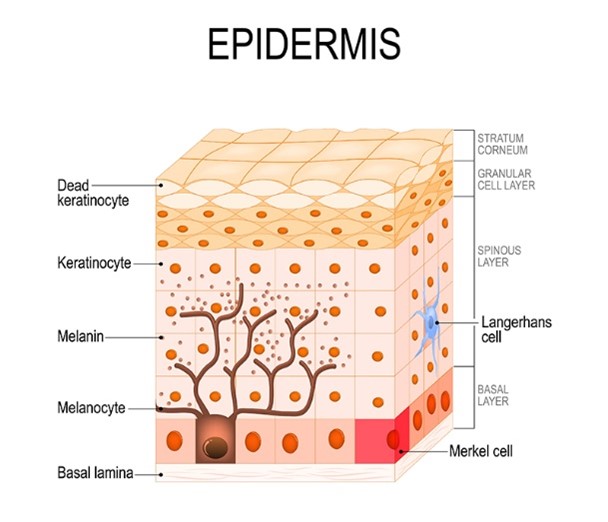

What causes Pigmentation?
Many forms of pigmentation result from prolonged sun exposure, even when you’re indoors near windows. While glass blocks UVB rays responsible for tanning, it still allows UVA rays to pass through, contributing to skin aging and pigmentation concerns.
What you need to know
Can skin pigmentation can be reversed?
You can noticeably lighten certain skin pigmentation issues like freckles and melasma by taking simple sun-smart steps, such as:
- Stay out of the sun during peak hours of the day.
- Wear protective gear like hats, sunglasses, long sleeves, and carry an umbrella when you’re outside.
- Use daily sunblock on your face, preferably with SPF 50 and UVA protection. Make sure to apply enough to cover pigmentation-prone areas of your face.
What are the common types of benign skin pigmentary disorders?
These include the following (list is not exhaustive)
- Moles and seborrheic keratosis: Moles are typically small, pigmented skin growths, while seborrheic keratosis are non-cancerous skin growths that often appear as waxy, brown or black raised spots.
- Lentigenes: Brown, small patches that show up on areas exposed to the sun, such as your face, arms, and legs, are called solar lentigines. They form as a result of long-term sun exposure and are harmless, posing no risk of turning cancerous. If you want to remove them, pigment laser treatment is an effective option.
- Horis naevi: These are moles surrounded by a ring of depigmented or lighter skin.
- Melasma: It is a common issue that leads to facial pigmentation. You’ll typically notice brown patches on your cheeks, forehead, upper lip, and nose bridge. While hormonal shifts like pregnancy or taking birth control pills can play a role, sunlight remains the primary trigger for melasma. Although melasma can come back, rest assured there are effective treatments to manage it.
What is the treatment of pigmentation?
If pigmentation affects an exposed site, daily application of a broad-spectrum SPF 50+ sunscreen is important to minimise darkening caused by UV radiation. Camouflage creams e.g. BB, CC or DD creams can be used as well.
Treatment options include topical pigment creams (hydroquinone, retinoids, steroids, vitamin C, etc.), chemical peels, laser and light treatments. Please see the respective treatment subpages for more details.