Treatments
Acne Scars
Overview
What is acne?
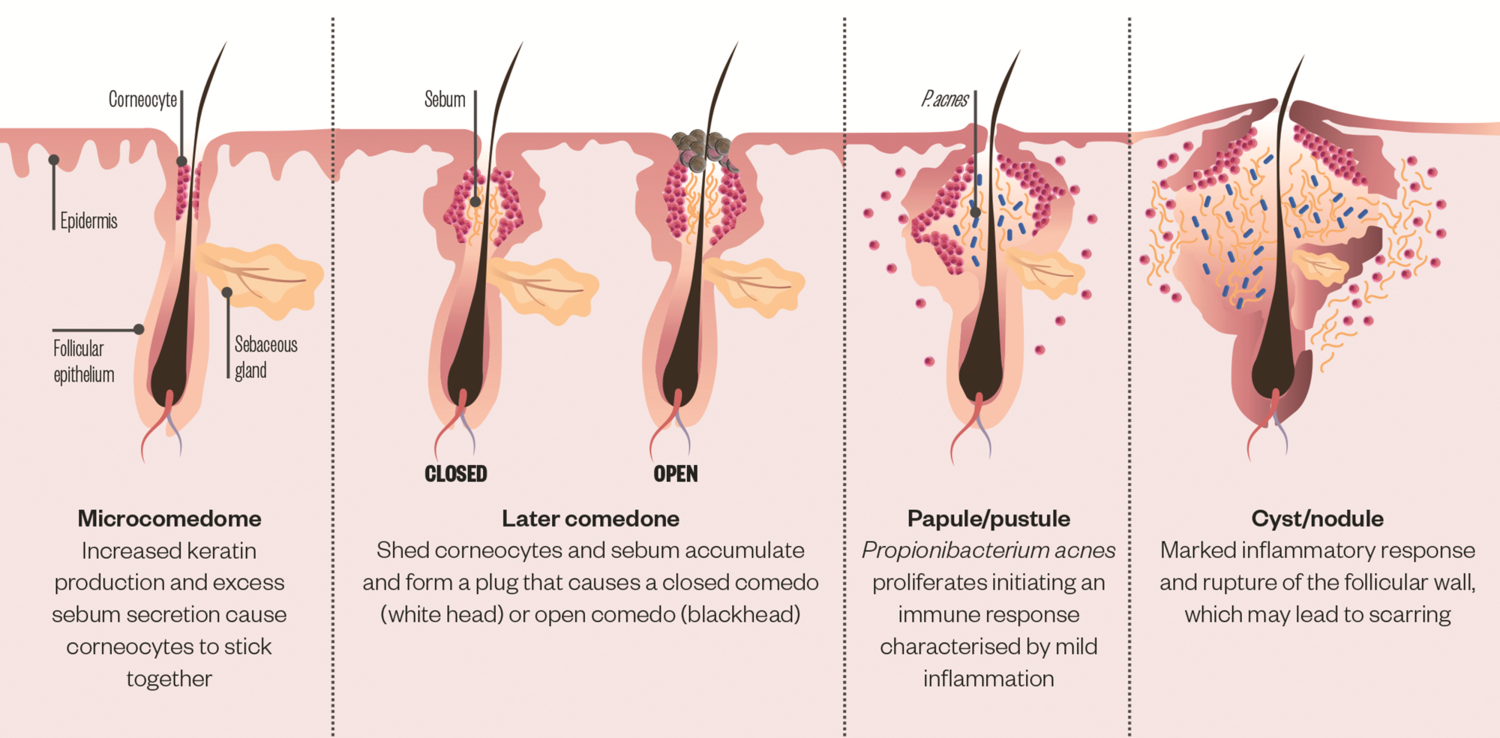
Acne is a common skin condition affecting the hair follicle and sebaceous gland, in which there is expansion and blockage of the follicle resulting in inflammation.


What you need to know
Who gets acne?
It affects both males and females of all races and ethnicities, more commonly in adolescent young adults with the majority (~85%) of 16 to 18 year olds affected. However, it can sometimes occur in children and adults of all ages.
What causes acne?
It can be due to a combination of factors as follows (list is not exhaustive)
- Familial tendency
- Hormones
- Acne bacteria
- Distension and occlusion of hair follicles
What are the clinical features of acne?
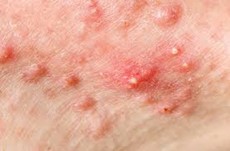
It is usually confined to the face, but it may involve the neck, chest and back. It is characterized by the following
- Comedones (blackheads and whiteheads)
- Inflamed papules and pustules
- In severe acne – nodules and cysts
- Post-inflammatory pigment and scars
- Severe social and psychological effects
It’s severity is broadly classified into mild, moderate and severe. The severity will normally guide the treatment recommendations.
What are the treatment options for acne?
It will depend on the severity. Treatment options include e.g. topical creams (retinoids), oral medications (antibiotics, isotretinoin) and procedures (Agnes, lasers), etc.
Understanding
What are acne scars?
They are a result of the normal healing process of inflammatory acne lesions e.g. nodules and cysts. Fibrosis occurs with new collagen laid down to heal a full-thickness injury. It affects roughly 30% of those with moderate to severe acne vulgaris. To reduce the chances of scarring, seek treatment early.

What you need to know
What is post inflammatory erythema, hyper and hypo pigmentation?
Post inflammatory colour changes are seen after inflammatory acne lesions have recently healed. Post inflammatory erythema are pink and purple flat patches. Post inflammatory pigmentation are brown marks that occur in mainly darker-skin individuals. Post inflammatory hypopigmentation are white marks on the skin.
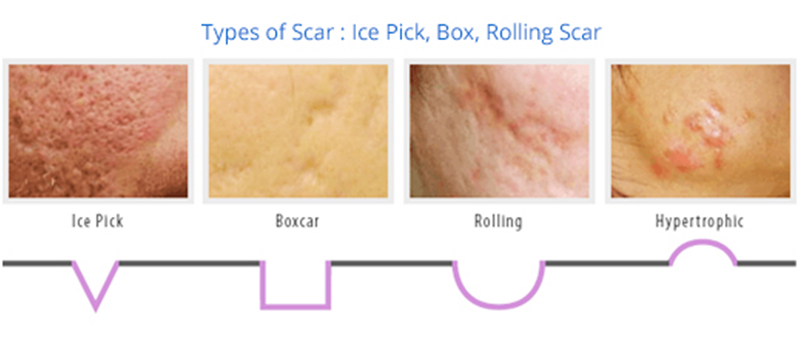
What are the different types of acne scars?
1. Ice-pick scars – they have a deep, narrow and pitted appearance
2. Rolling scars – broad depressions with slopping edge
3. Boxcar scars – broad depressions with sharply defined edges
4. Atrophic scars – have a flat, thin or depressed appearance
5. Hypertrophic or keloid scars – red, dark appearance and they are raised above the skin which can sometimes feel lumpy